Introduction to desulfurization process of power plant
2025-03-26 17:00:49
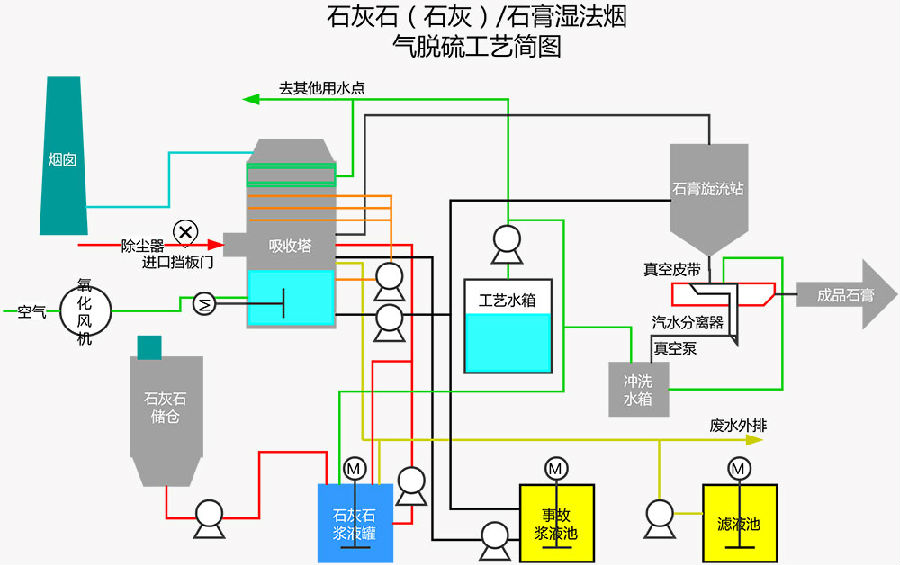
1. Limestone-gypsum flue gas desulfurization wet process (FGD)
This process uses limestone as desulfurization absorbent. The limestone is crushed and ground into powder and mixed with water to make absorption slurry. In the absorption tower, the absorption slurry contacts and mixes with the flue gas. The sulfur dioxide in the flue gas reacts chemically with the calcium carbonate in the slurry and the oxidizing air blown in to absorb and remove sulfur dioxide. The final product is gypsum. The desulfurized flue gas is dehydrated by the demister and heated by the heat exchanger before entering the chimney and being discharged into the atmosphere.
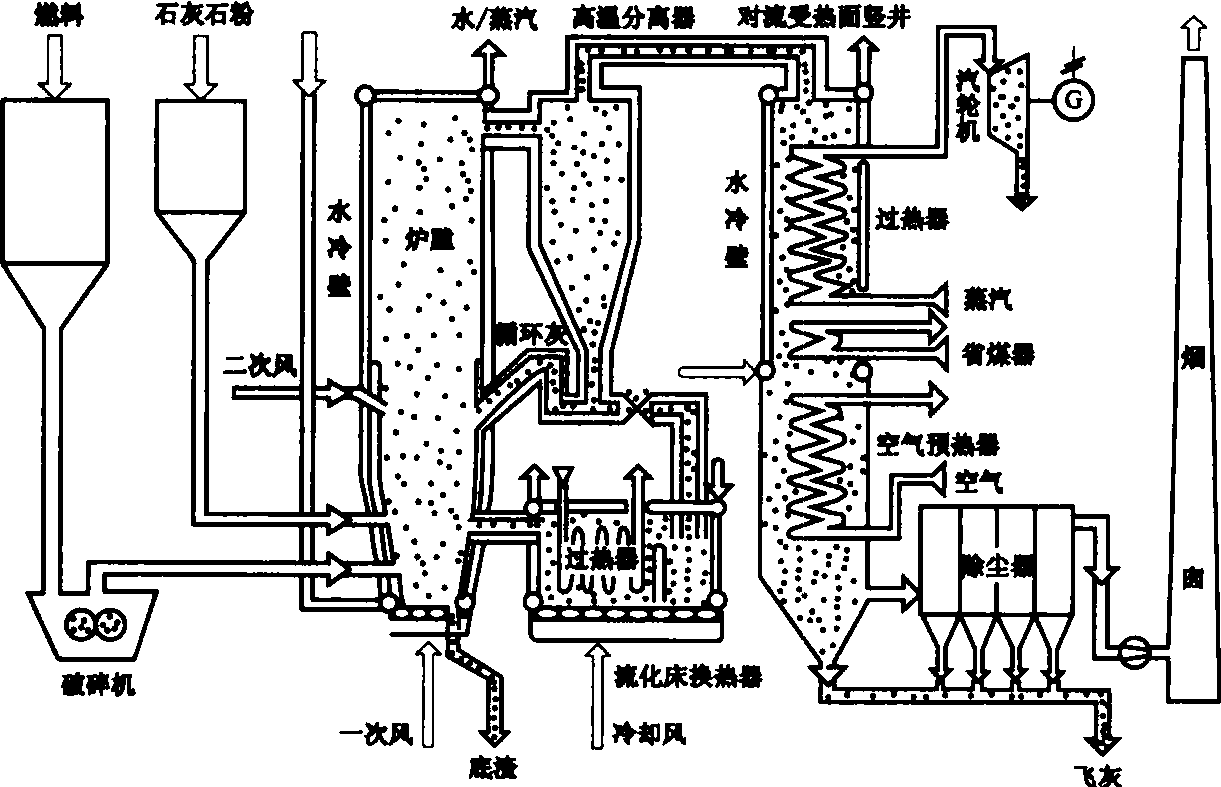
2. CFB circulating fluidized bed furnace in-furnace and out-furnace desulfurization process
In recent years, the desulfurization methods of newly built circulating fluidized bed power plants generally adopt a combination of in-furnace desulfurization and out-furnace flue gas desulfurization. It can fully utilize the convenience and low cost advantages of in-furnace desulfurization, and further purify the flue gas with the help of out-furnace flue gas desulfurization.
1. In-furnace desulfurization: The fuel and limestone are sent into the furnace together. In the fluidized combustion at 850-900℃, the limestone is decomposed into calcium oxide by heat, which reacts with sulfur dioxide in the flue gas to form calcium sulfite, which is discharged with ash.
2. Out-of-furnace desulfurization: After the flue gas enters the tail flue, semi-dry or wet secondary desulfurization is adopted. The semi-dry method sprays lime slurry to react with sulfur dioxide to form sulfate; the wet method absorbs sulfur dioxide through slurry washing and generates gypsum for recycling.